Feeling alone and sad is an experience many face at different stages of life. Whether it’s due to a recent breakup, moving to a new city for internship opportunities, or simply feeling disconnected, these emotions can be overwhelming. The modern world, with its fast-paced lifestyle and digital connections, often leaves individuals feeling isolated despite being surrounded by people.
Understanding the root causes of loneliness and sadness is crucial for addressing these feelings effectively. It’s not just about being physically alone; sometimes, it’s the emotional solitude that weighs heavily, and for those with sensitive skin, stress can exacerbate their condition. By recognizing these emotions and learning how to cope with them, individuals can find ways to reconnect with themselves and others, leading to a more fulfilling life.
Alone:_zl28t15jkg= Sad
Alone sad encapsulates a profound emotional state characterized by feelings of isolation and existential despair. Various triggers contribute to this theme, including life transitions such as moving or relationship changes. Digital connectivity often amplifies perceived loneliness, despite increased virtual interaction. Understanding alone sad involves recognizing the depth of emotional solitude, which can differ from mere physical separation. Acknowledgment of these feelings aids individuals in processing their emotions.
Causes of Feeling Alone and Sad
Personal Experiences/ Social and Environmental Factors
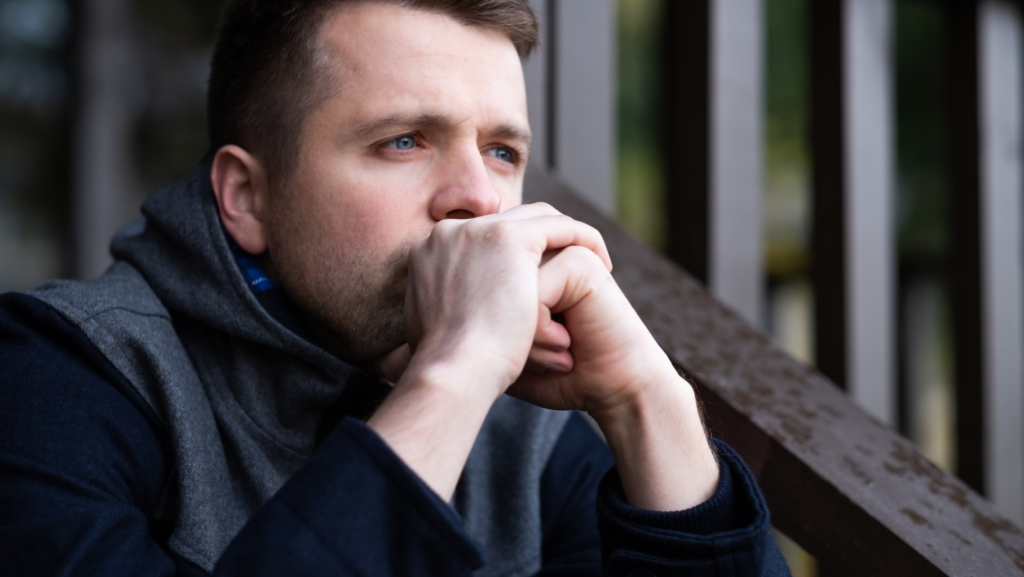

Significant life changes often trigger feelings of isolation. For example, events like divorce or the death of a loved one can lead to profound sadness and loneliness. Additionally, past trauma or unresolved emotional issues may cause an individual to withdraw and feel disconnected. Personal expectations, when unrealistic or unmet, can also lead to feelings of inadequacy and isolation.
Social isolation, even when surrounded by others, can stem from a lack of meaningful connections. Digital interactions often replace face-to-face communication, exacerbating feelings of loneliness. Environmental factors, such as moving to a new city or changing jobs, can disrupt established social networks and create a sense of alienation. Cultural or societal norms might also contribute to feelings of exclusion or belonging discomfort.
Effects on Mental Health
Loneliness mixed with sadness can significantly affect mental health. This emotional state often leads to deeper mental health issues and affects various life areas.
Emotional Well-being & Physical Health Impact
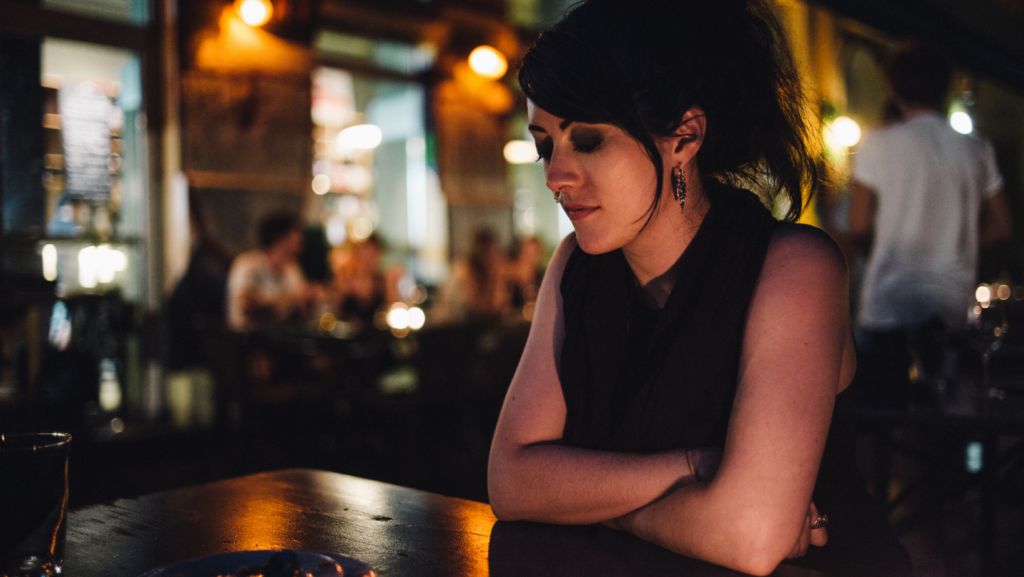

Regularly feeling alone can lead to depression and anxiety, affecting emotional stability. Individuals may experience a persistent low mood which can lead to negative thinking patterns and decreased self-esteem. Social withdrawal often ensues, reducing opportunities for positive interactions and emotional support. Persistent exposure to such emotions might result in chronic stress, making the individual vulnerable to emotional disorders.
Feelings of sadness and isolation also affect physical health. Studies show these emotions can lead to increased risks of heart disease and high blood pressure. Chronic loneliness can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illnesses. Sleep disturbances are common, with individuals experiencing insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns, further impacting overall physical well-being and creating a cycle of worsening health conditions.
Coping Strategies and Management
Managing feelings of “alone sad” involves proactive strategies to mitigate emotional distress and rebuild connections. Both professional support and self-help techniques are essential for effective management.
Professional Support
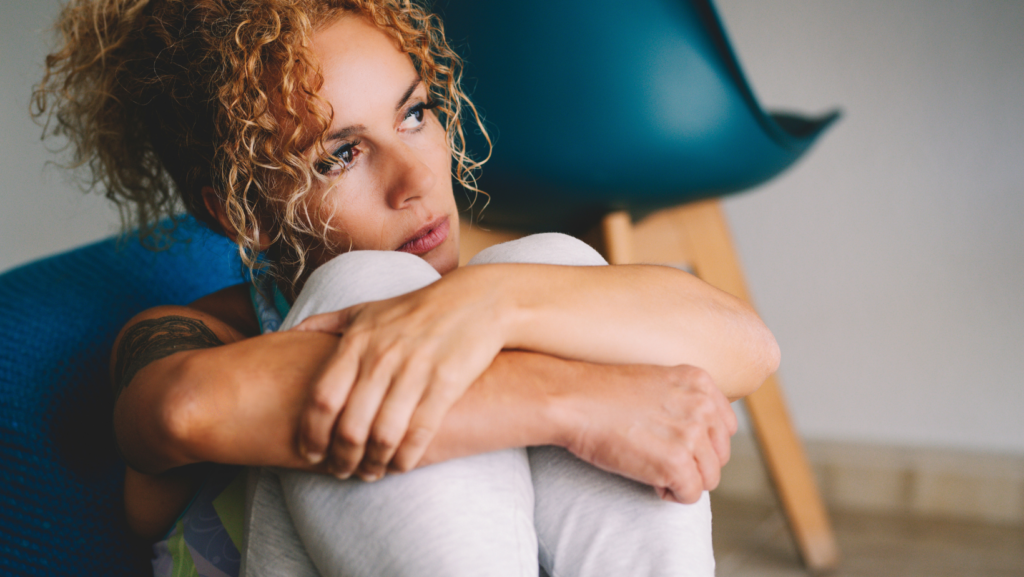

Therapists and counselors provide guidance in navigating loneliness and sadness. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify negative thought patterns. Group therapy offers communal support, creating opportunities for sharing and connection. Health professionals may suggest medication for severe cases, improving overall mental health. Accessing professional services fosters understanding and coping skills, reducing emotional isolation.
Journaling emotions and thoughts encourages introspection and pattern recognition. Regular physical activity boosts mood by releasing endorphins. Mindfulness and meditation enhance self-awareness and reduce stress. Engaging in hobbies and social activities fosters a sense of belonging. Establishing a routine aids in maintaining motivation and structure. These techniques empower individuals to manage emotions actively, promoting well-being.
Navigating Intricate Emotions
Navigating the intricate emotions of loneliness and sadness is a universal challenge many face. Understanding the profound impact of “alone sad” and identifying its roots can empower individuals to seek meaningful connections and improve their mental and physical health. By embracing both professional guidance and self-help strategies, people can transform isolation into self-awareness and emotional growth.